Differences in the neural wiring across the development of men and women across ages, matched behavioral differences
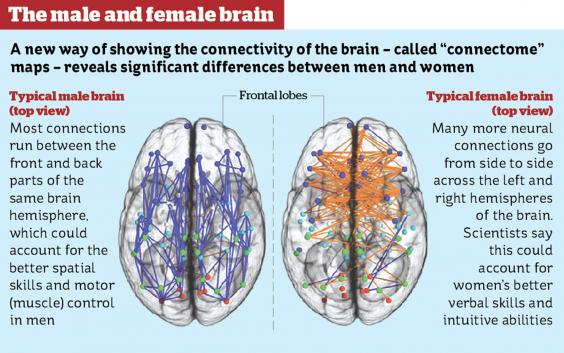
According to an imaging-based study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, differences in the neural wiring across the development of men and women across ages, matched behavioral differences commonly associated with each of the sexes.
The Penn team, including senior author Ragini Verma, PhD, performed diffusion tensor imaging brain scans and administered a computerized neurocognitive battery of tests on 900 randomly selected healthy and unmedicated Philadelphian children and young adults between the ages of 8 and 22, in order to find how structural differences in the brain may relate to male and female behavior differences such as men being more likely to be better at learning and performing a single task at hand and women being more likely to exhibit superior memory and social cognition skills. These methods allowed the team to develop a structural connectome, akin to a road map of each subject’s brain.
Understanding sex differences has long been an important quest in the medical industry, and is crucial to gaining an insight into the growing field of personalized medicine. The findings also have potential implications for treatment of a variety of conditions. The differences between men and women concerning diseases and disorders influence treatment of conditions such as autism, which is more common in men, as well as schizophrenia, which is also more frequent in males. It shows that the onset and severity of the disease alter greatly between the sexes.
‘Links between brain and behavior possibly rely on a complex interplay among multiple features of the neurobiological mechanism,” Verma said. “Network theoretical studies pertaining to the properties of the structural connectome may provide pioneering insights to these links.”
Get Started
Request Pricing Today!
We’re here to help! Simply fill out the form to tell us a bit about your project. We’ll contact you to set up a conversation so we can discuss how we can best meet your needs. Thank you for considering us!
Great support & services
Save time and energy
Peace of mind
Risk reduction
Sex-related differences in the connectivity of the subnetworks that were defined based on structural characteristics, functional systems, and finally, behavioral domains. Subnetworks are clusters of brain regions and their connectivity, which are associated with functionality or behavioral domains such as motor abilities, social motivation, or cognitive control.
During a 2013 study for the Proceedings of the Academy of Sciences, they discovered the neural wiring differences of men and women. But this study goes even further, reporting that differences in the behaviors of men and women are accompanied by related differences in the brain subnetworks. Stronger structural connectivity in motor, sensory, and executive functions matched higher motor and spatial skills in males, while in females, subnetworks associated with social cognition, attention, and memory tasks had higher connectivity and matched improved memory and social cognition skills.
“On a macro level, behavior-related disorders manifest and progress differently based on sex, and these findings should advance conversations about how we manage some of those conditions,” Verma said. “Our results suggest a synchrony between sex-related differences in the brain network and behavior. Thus, in a near future, we may be able to pinpoint precisely at the subnetwork level what we know about an individual’s brain and how to manage care of whatever disorders or ailments they are facing.”